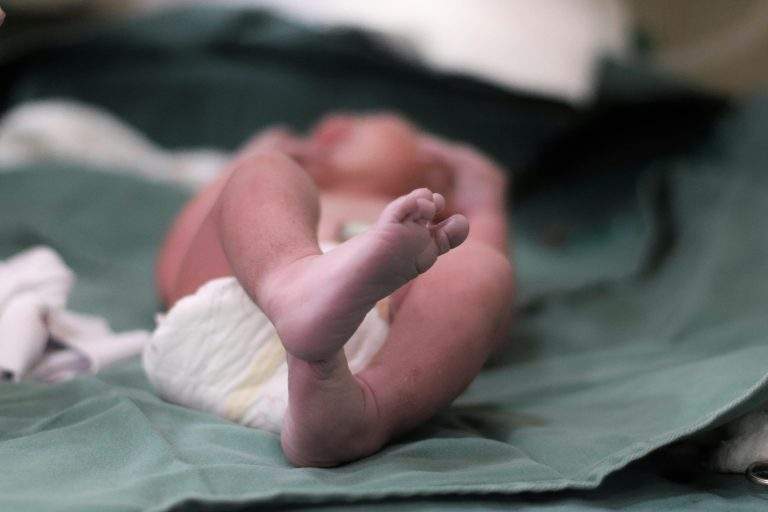
The NHS’s maternity shortcomings have once again caused significant sadness and widespread outrage throughout the United Kingdom. Families who lost children as a result of structural flaws in maternity care speak out, demanding accountability, transparency, and immediate change. Thus far, the ongoing inquiry into maternity and newborn services has shown some unsettling trends of avoidable damage and recurring care failings that never should have happened.
Growing National Outrage
The difficulties in NHS maternity care were widely acknowledged in recent months by an independent inquiry focused on maternity and baby healthcare across the country. The investigation, headed by Baroness Valerie Amos, heard the horrific accounts of poor staff management and listening, as well as challenges during pregnancy and childbirth.
Healthcare leaders are now acknowledging that there are nearly 750 prior recommendations pertaining to safety in maternity and neonatal units, which many NHS trusts have yet to implement. They also acknowledge that the pace of change in maternity units has been glacial and that many serious issues remain unresolved.
Real Cases Behind the Headlines
Such outrage is not based on statistics, but on the tragic loss of life.
Families in England have expressed their experiences of babies dying or being seriously harmed due to inadequate clinical care. Such cases have been reported to include preventable deaths, failing to recognise warning signs, and failing to listen to concerns raised by mothers concerning their babies’ movement or responding quickly to emergencies. Various investigations have shown that some hospital maternity units have been unable to provide basic care to their patients, such as paying attention to their mothers’ concerns about their babies’ movements.
In other instances, enforcement actions have revealed failures in individual trusts. The Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust, for example, was found guilty on six counts of failing to provide safe treatment for women and their infants following many instances of babies dying soon after birth as a result of risky practices.
Inquiry and Accountability
Following these incidents, the UK government and the NHS swiftly and thoroughly investigated the issue nationwide in order to determine the facts and offer remedies. According to Wes Streeting, the UK’s Health Secretary, the investigation aims to prevent further deaths while also giving families the truth and accountability.
These suggestions will subsequently be translated into action plans by the national maternity taskforce, which is made up of clinical specialists, families, and legislators. This will entail taking quick steps to raise safety standards and alter the NHS’s culture.
Long-standing Problems Still Unaddressed
Numerous watchdogs have cautioned that maternity shortcomings are still frighteningly pervasive after years of investigations and reviews.
Nearly half of maternity units assessed by the CQC needed to be improved or were graded as inadequate, indicating ongoing safety hazards, inadequate incident learning, and underfunded services.
Furthermore, reports from parliament and the Ombudsman show a sharp rise in maternity investigations, many of which were upheld because of deficiencies in diagnosis, communication, aftercare, and consent. These persistent patterns show that despite health investments, appropriate remedial measures have not been implemented for fundamental recurrent problems.
Families Still Demand Justice
However, the emotional toll of losing a baby goes far beyond the news. The families concerned have repeatedly called for thorough investigations, lucid explanations of what went wrong, and responsibility for those who are at fault. As more extensive investigations, such as independent reviews and judicial probes, continue to take place, these calls have become more urgent.
In order to help rebuild trust in maternity care, advocates and attorneys for the impacted families feel that open inquiry procedures and genuinely listening to grieving parents must come first. Many people think that more lives will be in danger until significant reform is put into place.
NHS
The NHS is at a pivotal point:
We think there is a unique chance to make long-lasting changes to the way we offer maternity and newborn services because of the continuing national investigation into maternity services, the growing regulatory requirements, and the strong advocacy from impacted families.
Despite their steadfast attempts to convince lawmakers and medical professionals that the care and attention given to women and their newborns in the UK should be normal, families who have suffered such a tragic loss cannot wait for these reforms to be put into place.